Difference between revisions of "Veerya"
| Line 270: | Line 270: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | </p> | + | The assessment of the gurvadi guna as type of veerya can be studied through the effect they depict on the metabolism of body and body tissues. Qualitative assessment through the means of questionnaires or interviews is more commonly done recently. Amongst the 20 guna, snigdha (unctuous) and ruksha (dryness) guna are more extensively studied. For instance, sneha guna is assessed by determining the presence of snidghata or oiliness or unctuousness of skin and the contrary for ruksha guna.<ref name="ref7">Mishra S, Dwivedi RR, Ravishankar B. Conceptual and applied study of Snigdha and Ruksa Guna with special reference to Rasa-raktagata Sneha (hyperlipidemia). Ayu. 2011;32(2):200-206. doi:10.4103/0974-8520.92586</ref> Biochemical parameters like lipid profile are also used to determine the sneha guna in the body. Similaly the cell line studies are conducted to study the snigdhata in terms of adipocytic and anti-adipocytic activity in herbs like Terminalia belerica.<ref name="ref8">Ruchika Dighekar, Kiran Tawalare, Dr. Pankaj Jogi. A Biochemical Approach to Understand the Concept of Snigdha Guna of Ghee and Ruksha Guna of Terminalia Arjuna on Behaviour of 3T3-L1 Cell Line with Respect to Adipocytic and AntiAdipocytic Activity : In Vitro. J Ayurveda Integr Med Sci 2020;6:73-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.21760/jaims.5.6.9</ref> The different tools and instruments like glossometer, and sudometer can be used in the assessment of snigdha and ruksha guna. The assessment of basic panchabhoutika structure can also help in assessment of guna. The organoleptic assessment can also help in determining the general quality of dravya. However, there is immense scope for creating more evidence to prove the veerya in gurvadi guna.<ref name="ref9">Guna [Internet]. Charak Samhita. 2022 [cited 2023 Jan 20]. Available from: https://www.carakasamhitaonline.com/index.php?title=Guna</ref></p> |
| + | |||
| + | === Two main types of veerya (dwividha veerya vaada) === | ||
| + | <p style='text-align:justify;'>Most of the scholars accepted two types of veerya (the dwividha veerya vaada). The hot and cold are considered as two main contrasting energies responsible for carrying out various functions in body. These can be equated to soma and agni i.e. the moon and the sun in the universe. These also represent the concept of Yin and Yang as put forth by traditional Chinese medicine.<ref name="ref10">Fu R, Li J, Yu H, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Martin C. The Yin and Yang of traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Medicinal Research Reviews [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Jan 20];41(6):3182–200. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/med.21793</ref> The three dosha are either considered to sheeta (kapha , vata dosha) or ushna (pitta dosha) in nature. The approach of ayurveda regarding two types of veerya can be summarised as below:<br/>1. Although all the dravya are panchabhautika in nature they can either be divided as ushna (hot) or sheeta (cold) based on the dominancy of ushna and sheeta guna [A.H. Sutra Sthana .9/17, Indu commentary on A.S. Sutra Sthana 1/26] <br/>These can be considered the most suitable types of veerya which can also be equated to karya-karana hetu according to ayurveda. These two are best representatives of the dual energy i.e. heat and cold in the universe and hence rightly termed as dwividha veerya.[ A.H. Sutra Sthana 9/17] <br/>There are two other types of veerya: kritrima (artificial) and sahaja (inherent) veerya. Shivadas sen quotes the example of the heaviness of black gram (masha) and lightness of green gram (mudga) for inherent veerya (sahaja veerya), while that of lightness of puffed paddy (laja) to explain the aritificial veerya (kritrima veerya). [Chakrapani on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/66 <br/>Shivadas Sen commentary on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/65] </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Different theories pertaining to concept of veerya (veeryavada) == | ||
| + | <ol style='text-align:justify;' type="a"> | ||
| + | <li style="font-weight:bold">Action-based potency (karma veerya vaada):<br/><span style="font-weight:normal">The potency of a dravya is observed according to its major pharmacotherapeutic actions. [Bhadanta Naagaarjuna in Rasavaisheshika]<ref name="ref11">Nagarjuna B. Bhadanta nagarjuna’s Rasavaisheshika text with English translation by K Raghavan Tirumulpad, Arya Vaidya sala, First Edition. Kozhikode, India: Geetanjali Offset Prints; 2013, Page No. 228</ref> Certain veerya such as emetic (Chhardaneeya veerya), carminative (Anulomana veerya) etc. are described. Fifteen types of Veerya are described by Acharya Nimi.<ref name="ref12">D.S. Lucus, Dravyagunavijnana (Basic principles of Dravyaguna, Vol.I, Chapter Veerya Vijanana, Chaukhambha Vishwa Bharathi, Varanasi, First edition, 2006, page No. 218/455.</ref></span></li> | ||
| + | <li style="font-weight:bold">Quality-based potencies (Guna Veerya Vaada or Shakti Veerya Vaada):<br/><span style="font-weight:normal">The quality based action (Guna Veerya Vaada or Shakti Veerya Vaada) is as described above.</span></li> | ||
| + | <li style="font-weight:bold">Substance (dravya veerya vaada):<br/><span style="font-weight:normal">Veerya is a special power of dravya that is capable of performing actions.[Shivadasa Sen] The ability of rasa, vipaka, or prabhava to perform any action is termed veerya. However, dravya and veerya are different as veerya resides in dravya. [Shivadas Sen commentary on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/64-65]</span></li> | ||
| + | <li style="font-weight:bold">Paribhashika veerya vaada:<br/><span style="font-weight:normal">The two types and eight types of veerya (dwividha veeryavada and ashtavida veerya vada) are considered under the heading of paribhashika veerya vada. It is mentioned by Charak and Vagbhata.</span></li></ol> | ||
<big>'''[[Special:ContactMe|Send us your suggestions and feedback on this page.]]'''</big> | <big>'''[[Special:ContactMe|Send us your suggestions and feedback on this page.]]'''</big> | ||
Revision as of 18:19, 3 February 2023
Veerya (also spelled as Virya) means potency or active components. The ayurvedic pharmacological principles include five factors, viz. rasa (taste), guna (qualities), veerya (potency), vipaka (post-digestive effect), and prabhava (significant effect). These are commonly known as rasa-panchaka or dravyagat pancha padartha.[1] Veerya is one of the crucial factors in constituting the pharmacology of drug. In pharmacology, as per Ayurveda, the word Veerya [SAT Code- F.22] is envisaged as the potential factor of the drug by which it performs specific actions in the body. This broad term is employed to explain lesser or greater potential drug factors concerning different processes and procedures to achieve the desired effect in the body.[2]
| Section/Chapter/topic | Concepts/Veerya |
|---|---|
| Authors |
Bhojani M. K. 1, Joglekar Aishwarya 2, Joshi Sumedh 3 |
| Reviewer | Basisht G.4, |
| Editor | Deole Y.S.5 |
| Affiliations |
1 Department of Sharir Kriya, All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi, India 2 Department of Samhita Siddhant, All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi, India 3Department of Dravyaguna, All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi, India 4 Rheumatologist, Orlando, Florida, U.S.A. 5 Department of Kayachikitsa, G. J. Patel Institute of Ayurvedic Studies and Research, New Vallabh Vidyanagar, Gujarat, India |
| Correspondence emails |
meera.samhita@aiia.gov.in, carakasamhita@gmail.com |
| Publisher | Charak Samhita Research, Training and Development Centre, I.T.R.A., Jamnagar, India |
| Date of publication: | Febraury 04, 2023 |
| DOI | 10.47468/CSNE.2023.e01.s09.127 |
Etymology
The term ‘Veerya’ is derived from the grammatical Sanskrit root ‘Veer’ or ‘Vri’ meaning ‘Vikranti’ or specific power to express vigour, strength etc.[3] Monnier Williams dictionary[4] mentions veerya means vigour, strength, power; heroism, prowess, valour, fortitude, courage, firmness; virile energy, virility; dignity, consequence; splendour, lustre, vigour, energy and virility. It also synonymous with terms like shukra dhatu (reproductive components including semen, virility), param dhatu (ultimate dhatu, nectar of all the dhatu), shakti (potency), dravya karma (drug action), prabhava, parakrama (valour or courage) as termed in Vachaspatyam.[5]
Synonyms
Shakti, prabhava, samarthya [Dalhana on Su.Sa.Sutra Sthana 40/1] bala, and gunotkarsha [Chakrapani on Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana .40/3]
Characteristics
Dravya is classified into two types: rasa pradhana (dominated by rasa) and veerya- pradhana (dominated by veerya). [Chakrapani on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 2/17] The dietary items (ahara dravya) are considered rasa pradhana, while medicines (aushadha) are deemed to be veerya pradhana. The aushadha are again divided into three types based on veerya, namely mild (mrudu veerya), moderate (madhyama veerya) and sharply acting (teekshna veerya) [Chakrapani on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 2/17]. This can be summarised in the table given below:
| Veerya wise classification | Examples | Matra (dose) to be used |
|---|---|---|
| Teekshna veerya | Shunthyadi (herbs like Shunthi- Zingiber offincinale) | Karsha (12 grams) |
| Madhyama veerya | Bilva-agnimanthadi (herbs like Bilva- Aegle marmelos and Agnimantha- Premna serratifolia etc.) | Ardhapala (24 grams) |
| Mridu veerya | Amalakadi (herbs like Amalaki- Phyllanthus emblica) | Pala (48 grams) |
| Sr. No | Author name | Opinion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Charak | Considers chintya (explainable) and achintya (unexplainable) veerya. | Cha. Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/70 |
| Defines veerya as the potency or power of the drug through which it performs its work or action | Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana.26/65 | ||
| 2. | Sushruta | Denoted veerya as the generator of a drug action | Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana.40/3 |
| 3. | Dalhana | Karma (action) that cannot be performed by dravya, rasa, guna, or vipaka is veerya. Veerya is activity potential or karyashakti of dravya. | Dalhana on Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana.40/3 |
| 4. | Chakrapani | The term veerya is meant for all rasa, guna, vipaka, or prabhava of a dravya | Chakrapani on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/64-65 |
| Divides the veerya into chintya and achintya, where the latter can be termed as the prabhava of a particular dravya. | Chakrapani on Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana.40/5 | ||
| 5. | Arundatta | The prominence of ushna guna will lead to development of ushna veerya, while sheeta guna prominence results in sheeta veerya. | Arundatta on A.H. Sutra Sthana.1/17 |
| 6. | Hemadri | The digestion and metabolism (kayagnipaka) leads to the development of eight guna, amongst which sheeta and ushna are considered the most dominant termed as ushna and sheeta veerya. It is termed as shakti arising from the transformation of guna. | Hemadri on A.H. Sutra Sthana.1/17 |
| 7. | Shivdas Sen | Veerya is the the most supreme and nectar part (atishaya sara bhaga) of the panchamahabhuta, further dividing it into chintya and achintya. | Shivadas Sen on Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana.40/5 |
| 8. | Bhavamishra | Bhavamishra has clearly differentiated the veerya from prabhava. He quotes the prabhava as shakti of the drug. | Bhavamisra, Bhavaprakasha with commentary by Dr Bulusu Sitaram, Mishra-Prakarana, Poorvakhanda, Shloka Number 161, Volume 1, Reprinted 2015, Chaukhamba Orientalia, Varanasi Page No. 117 |
| 9. | Acharya Yadavji Trikamji | Interprets veerya as the active principle of the drug.[6] | Acharya Yadavaji Trikamji, DravyaGuna Vidnyanam, Poorvardha,Published by Nirnay Sagar Press, Bombay Page no 249-277 |
| 10. | Prof P.V.Sharma | The active principle is also a dravya and veerya being a type of guna cannot be equated with active principle | PV Sharma, DravyaGuna vijnana, Vol I, Chaukhambha Bharti Academy, Varanasi, Edition year 2013, Page no 263-278 |
| 11. 13. | Prof. C. Dwarkanath | The term veerya conveys the idea of energy. The energy of a body is its capacity for doing work and the measure of energy is work. Energy may be potential or kinetic,2 where the sheeta veerya can be considered as potential energy, while ushna veerya as kinetic energy. | Veerya A general principle of drug action [Ayusoft] 2 |
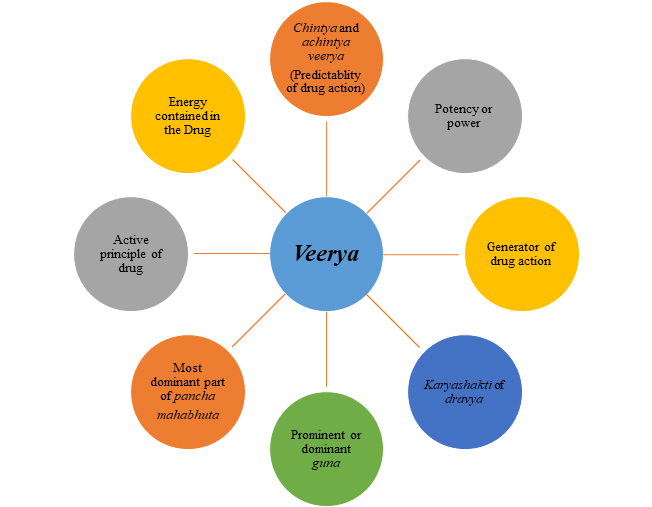
Thus in order to summarize various forms of veerya can be depicted in following figure-
Types of veerya
Charak and Sushruta Samhita mention the eight types (ashtavidha) and two types (dwividha veerya) of veerya. However, emphasis is given on the two types (dwividha veerya) [Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/64, Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 40/5]. Other types can be considered as chintya-achintya and sahaja-kritama as mentioned in the previous point.
Eight types (ashtavidha veerya vaada)
Ashtavidha veerya or eight types of veerya are as below:
- Guru (heaviness)
- Laghu (lightness)
- Snigdha (unctuousness)
- Ruksha (dryness)
- Teekshna (piercing, sharp)
- Manda (slowness, mildness)
- Sheeta (coldness)
- Ushna (hotness). [Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/64]
These are considered as eight representatives of twenty gurvadi guna mentioned in the Samhita. These are also termed as guna possessing veerya like properties or guna named as veerya i.e. veeryakhya guna. Sushruta Samhita mentions the vishada and pichchhila guna in place of guru and laghu guna while stating the veerya. [Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 40/5]
The rationale behind ashtavidha veerya vaada can be discussed as given in the table below [Arunadatta on A.H. Sutra Sthana 9] :
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Samagra Guna Saarataa (Stability after metabolism) |
|
| Shaktyutkarshata (High potency of action) |
|
| Vyavahaara mukhyatva (More practical utility) |
|
| Bahulyataa dravya |
|
The effect of eight potencies (ashtavidha veerya) on dosha, probably contributing to systemic effects / therapeutic effects, can be described in the table below. These can be determined through the karma of dravya possessing the particular guna- (Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 46/515-524)
| Sr. No | Veerya | Effect on doshas | Systemic effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ushna (hot) |
Vata hara Kapha hara Pitta vardhaka |
Deepana (~appetizer), pachana (~digestive), dahajanana (~causes burning sensation), murchhana (~cause fainting), swedana (~induce perspiration) , vamanakarak (induce emesis), virechana (~purgative), vilayana (~escharotic), bhramakaraka (~induce giddiness), trushnajanana (~induce thirst), aashupaaka (~cause quicker digestion and suppuration), avrushya (~reduces fertile strength) |
| 2. | Sheeta (cold) |
Pitta hara Vata kapha vardhaka |
Prahlaadana (~soothing) , vishyandana (~secretogogue) , sthirikarana (~stabilizer), kledana (~moistening) , jeevaniya (~enhance life expectancy) , stambhana (~styptic), raktaprasadana (~enhances quality of rakta dhatu), balyam (~giving strength) |
| 3. | Snigdha (unctuous) |
Vata hara kapha vardhaka |
Snehana (~sudation), brimhana (~increases mass) , santarpana (~nourishing), vajikarana (~aphrodisiac), vayasthaapana (~increase viability) |
| 4. | Ruksha (dryness) |
Vata vardhaka, kapha pittahara |
Samgrahana (~astringent), peedana (~cause obscuration) , virookshana (~causing dryness), ropana (~cause healing) |
| 5. | Guru (heaviness) |
Kapha vardhaka vatahara | Upalepana (~cause act of smearing) , brimhana (~nourishing), balya (~strengthening) |
| 6. | Laghu (lightness) |
Kaphahara vatavardhaka | Lekhana (~cause scrapping), langhana (~cause lightness), dhatu kshaya (~ destruction of dhatus) |
| 7. | Mridu (softness) |
Pittahara | Rakta and mamsa prasaadana (enhances the quality of rakta and mamsa dhatu) |
| 8. | Teeksna (sharpness) |
Kaphahara | Sangraahi (astringent), aachushana (~absorbs unwanted secretions) , avadarana (~cause tearing), stravana (~secretogogue) |
| 9. | Vishada (cleansing) |
Kaphahara | Kledachooshana (~absorbs moisture), virookshana (~cause dryness), uparohana (~cause healing) |
| 10. | Pichchila (slimy) |
Kaphavardhaka | Upalepana (~cause act of smearing), Purana (~cause healing), brumhana (~increases mass), Samsleshara (~avoids binding to the dhatus), vajikarana (~aphrodisiac) |
| Type of veerya | Panchamahabhoota prominence | Method of assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Sheeta | Ambu (Jala) | Sparshagrahya (~assessed by touch) |
| Ushna | Agni | Sparshagrahya (~assessed by touch) |
| Snigdha | Prithvi + Ambu | Chakshugrahya(~assessed by visionary sense) |
| Ruksha | Vayu | Chakshugrahya (~assessed by visionary sense) |
| Mrudu | Jala + Aakasha | Sparshagrahya (~Assessed by touch) |
| Tikshna | Agni | Mukha dukhotpeedanat (~assessed by the effect on buccal mucosa) |
| Picchila | Jala | Chakshu+sparshagrahya (~assessed by visionary sense and touch) |
| Vishada | Prithvi + Vayu (Kshiti-sameerana) | Chakshu+Sparshagrahya (~assessed by visionary sense and touch) |
The assessment of the gurvadi guna as type of veerya can be studied through the effect they depict on the metabolism of body and body tissues. Qualitative assessment through the means of questionnaires or interviews is more commonly done recently. Amongst the 20 guna, snigdha (unctuous) and ruksha (dryness) guna are more extensively studied. For instance, sneha guna is assessed by determining the presence of snidghata or oiliness or unctuousness of skin and the contrary for ruksha guna.[7] Biochemical parameters like lipid profile are also used to determine the sneha guna in the body. Similaly the cell line studies are conducted to study the snigdhata in terms of adipocytic and anti-adipocytic activity in herbs like Terminalia belerica.[8] The different tools and instruments like glossometer, and sudometer can be used in the assessment of snigdha and ruksha guna. The assessment of basic panchabhoutika structure can also help in assessment of guna. The organoleptic assessment can also help in determining the general quality of dravya. However, there is immense scope for creating more evidence to prove the veerya in gurvadi guna.[9]
Two main types of veerya (dwividha veerya vaada)
Most of the scholars accepted two types of veerya (the dwividha veerya vaada). The hot and cold are considered as two main contrasting energies responsible for carrying out various functions in body. These can be equated to soma and agni i.e. the moon and the sun in the universe. These also represent the concept of Yin and Yang as put forth by traditional Chinese medicine.[10] The three dosha are either considered to sheeta (kapha , vata dosha) or ushna (pitta dosha) in nature. The approach of ayurveda regarding two types of veerya can be summarised as below:
1. Although all the dravya are panchabhautika in nature they can either be divided as ushna (hot) or sheeta (cold) based on the dominancy of ushna and sheeta guna [A.H. Sutra Sthana .9/17, Indu commentary on A.S. Sutra Sthana 1/26]
These can be considered the most suitable types of veerya which can also be equated to karya-karana hetu according to ayurveda. These two are best representatives of the dual energy i.e. heat and cold in the universe and hence rightly termed as dwividha veerya.[ A.H. Sutra Sthana 9/17]
There are two other types of veerya: kritrima (artificial) and sahaja (inherent) veerya. Shivadas sen quotes the example of the heaviness of black gram (masha) and lightness of green gram (mudga) for inherent veerya (sahaja veerya), while that of lightness of puffed paddy (laja) to explain the aritificial veerya (kritrima veerya). [Chakrapani on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/66
Shivadas Sen commentary on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/65]
Different theories pertaining to concept of veerya (veeryavada)
- Action-based potency (karma veerya vaada):
The potency of a dravya is observed according to its major pharmacotherapeutic actions. [Bhadanta Naagaarjuna in Rasavaisheshika][11] Certain veerya such as emetic (Chhardaneeya veerya), carminative (Anulomana veerya) etc. are described. Fifteen types of Veerya are described by Acharya Nimi.[12] - Quality-based potencies (Guna Veerya Vaada or Shakti Veerya Vaada):
The quality based action (Guna Veerya Vaada or Shakti Veerya Vaada) is as described above. - Substance (dravya veerya vaada):
Veerya is a special power of dravya that is capable of performing actions.[Shivadasa Sen] The ability of rasa, vipaka, or prabhava to perform any action is termed veerya. However, dravya and veerya are different as veerya resides in dravya. [Shivadas Sen commentary on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 26/64-65] - Paribhashika veerya vaada:
The two types and eight types of veerya (dwividha veeryavada and ashtavida veerya vada) are considered under the heading of paribhashika veerya vada. It is mentioned by Charak and Vagbhata.
Send us your suggestions and feedback on this page.
References
- ↑ Bhavamisra, Bhavaprakasha with commentary by Dr Bulusu Sitaram, Mishra-Prakarana, Poorvakhanda, Shloka Number 161, Volume 1, Reprinted 2015, Chaukhamba Orientalia, Varanasi Page No. 117
- ↑ Available from Veerya A general principle of drug action – Ayusoft. https://ayusoft.ayush.gov.in/veerya-a-general-principle-of-drug-action/ accessed on 31/01/2023
- ↑ RāDhāKāNtadeva, Vasu, V., & VASU, H. (1886).Śabdakalpadrumah , Page No. 474 Available from: https://www.sanskritlexicon.unikoeln.de/scans/SKDScan/2020/web/index.php
- ↑ Monier-Williams, M. (1872) , Page No.955, Available from https://www.sanskrit-lexicon.uni-koeln.de/scans/MW72Scan/2020/web/webtc/indexcaller.php
- ↑ Bhaṭṭacarya, T. V. (1873). Vacaspatyam: Brihat Saṃskṛtabhidhanam. 5 5. Varaṇasi, Chaukhamba Saṃskṛita Series office, Page No. 4944
- ↑ Acharya Yadavaji Trikamji, DravyaGuna Vidnyanam, Poorvardha, Published by Nirnay Sagar Press, Bombay Page no 249-277
- ↑ Mishra S, Dwivedi RR, Ravishankar B. Conceptual and applied study of Snigdha and Ruksa Guna with special reference to Rasa-raktagata Sneha (hyperlipidemia). Ayu. 2011;32(2):200-206. doi:10.4103/0974-8520.92586
- ↑ Ruchika Dighekar, Kiran Tawalare, Dr. Pankaj Jogi. A Biochemical Approach to Understand the Concept of Snigdha Guna of Ghee and Ruksha Guna of Terminalia Arjuna on Behaviour of 3T3-L1 Cell Line with Respect to Adipocytic and AntiAdipocytic Activity : In Vitro. J Ayurveda Integr Med Sci 2020;6:73-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.21760/jaims.5.6.9
- ↑ Guna [Internet]. Charak Samhita. 2022 [cited 2023 Jan 20]. Available from: https://www.carakasamhitaonline.com/index.php?title=Guna
- ↑ Fu R, Li J, Yu H, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Martin C. The Yin and Yang of traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Medicinal Research Reviews [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Jan 20];41(6):3182–200. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/med.21793
- ↑ Nagarjuna B. Bhadanta nagarjuna’s Rasavaisheshika text with English translation by K Raghavan Tirumulpad, Arya Vaidya sala, First Edition. Kozhikode, India: Geetanjali Offset Prints; 2013, Page No. 228
- ↑ D.S. Lucus, Dravyagunavijnana (Basic principles of Dravyaguna, Vol.I, Chapter Veerya Vijanana, Chaukhambha Vishwa Bharathi, Varanasi, First edition, 2006, page No. 218/455.